Thermic Effect of Food Calculator - Metabolic Impact Analysis
Calculate how many calories your body burns digesting food and optimize your diet for maximum metabolic benefit.
Nutrition Input
Meal Factors
TEF Calories
226
TEF Percentage
10.6%
Net Calories
1907
TEF Macronutrient Breakdown
TEF Distribution
Macronutrient Analysis
Optimization & Recommendations
Calorie Impact
High-TEF Food Recommendations
High-TEF Proteins
Highest thermic effect
- Chicken breast: 30% TEF
- Lean beef: 25-30% TEF
- Fish: 25-30% TEF
- Eggs: 25% TEF
- Greek yogurt: 20-25% TEF
Complex Carbs
Moderate thermic effect
- Oatmeal: 8-10% TEF
- Sweet potatoes: 8-10% TEF
- Brown rice: 7-9% TEF
- Quinoa: 8-10% TEF
- Legumes: 8-12% TEF
High-Fiber Foods
Enhanced digestion cost
- Broccoli: 15-20% TEF
- Berries: 10-15% TEF
- Avocado: 5-8% TEF
- Nuts: 5-10% TEF
- Chia seeds: 15-20% TEF
TEF Optimization Strategy
Related & Other Popular Calculators, Tools
If you are interested in enhancing your metabolism, naturally burn more calories, and learn how your food affects your body, the Thermic Effect of Food(TEF) Calculator is the tool for you. This simple yet effective calculator will provide an estimate of how many calories you burn during digestion - also referred to as the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) or diet-induced thermogenesis.
Using the Thermic Effect of Food Calculator, not only will you be able to determine how different macronutrients (proteins, carbs, and fats) help you burn calories, but you can also plan meals for optimum efficiency to help your metabolic efficiency and fat loss goals.
What is the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)?
The Thermic Effect of Food, or TEF, is the amount of energy your body uses to digest, absorb and process the nutrients you have consumed. Therefore, every time you eat a meal, your metabolism temporarily spikes - and this increase in calorie burning is the imagined thermic effect of food.
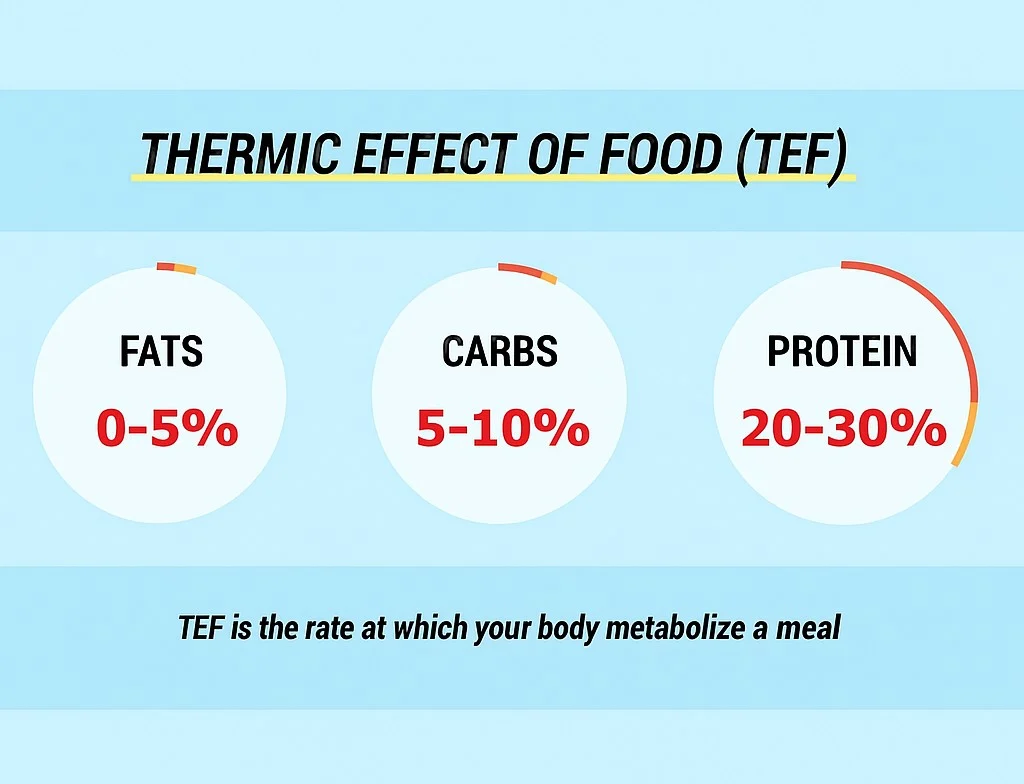
Each macronutrient has a different thermic effect:
This is why high protein diets often create a higher daily energy expenditure - your body works harder to digest food.
How the Thermic Effect of Food Calculator Works
Our Thermic Effect of Food(TEF) Calculator minimizes complex metabolic science into an easy, everyday experience.
So here is how it works:-
Why use the Thermic Effect of Food Calculator?
The Thermic Effect of Food Calculator isn't just a simple calorie calculator - its a unique systematic - scientific way of increasing your metabolism and optimizing nutrition. Here's what makes it a great tool in metabolizing food for fuel:
Here's what makes it invaluable:
Benefits of using the TEF Calculator
Whether you are fitness oriented, a nutrition coach, or just someone looking to have a healthy lifestyle, this is to help you make intelligent, data-driven, eating decisions.
TEF Optimization Tips
Here are practical ways to enhance your Thermic Effect of Food naturally:
All of these eating and exercise methods could integrate with our TEF Calculator and make your metabolism work smarter, not harder.
The Thermic Effect of Food Calculator is your ultimate guide to understanding metabolism and enhancing nutrition.
By exposing how different foods are processed teaches you ways to maximize calories burnt from energy or nutrition, in support of weight goals, and optimize metabolism.
FAQs
- The Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) Calculator is an estimate of how many calories your body would burn digesting and processing food. This is useful to understand what the calories you eat can do metabolically and how calories are burned.
- Our calculator relies on scientific averages for macronutrient thermic effects. While actual TEF varies a little per individual it is still highly reliable and accurate for general dietary planning and metabolic measurements.
- Yes! Protein has the highest thermic effect at intake and digestion, using roughly 20-30% of its calories to process versus 5-10% for carbs and 0-3% for fats.
- Sure! If excess calories are avoided, when eating foods with a high thermic effect, along with determining your macronutrients you can naturally increase calorie expenditure and enhance fat efficiency.
- The make-up of the food (macronutrient type and portions) the degree of processing, and you (metabolism) account for some variation in TEF. Whole, high-protein foods usually induce more thermic responses than others.
- Daily or weekly use is fine - but especially noticeable when you are adjusting your nutrition or switching meals. Frequent use allows you to assess your food intake in order to fine-tune your nutrition plan.